
The decision to retain or distribute earnings depends on a variety of factors, including the company’s stage of development, strategic priorities, and tax considerations. For many years, Apple retained a significant portion of its earnings to fund its rapid growth and innovation. However, as the company matured, it began to face pressure from shareholders to return more of its earnings as dividends and share buybacks. However, the relationship between undistributed profit and shareholder value is not always straightforward.
- They reflect the cumulative net income of the company after deducting dividends paid to shareholders.
- This, of course, depends on whether the company has been pursuing profitable growth opportunities.
- For instance, a company with $50 million in retained earnings and $200 million in total assets has a ratio of 25%, reflecting effective reinvestment strategies.
- When the dust settles at the end of the year, a business can generally do one of two things with excess cash.
- In the United States, the tax treatment of undistributed profit can influence a company’s decision to retain or distribute earnings.
- Such items include sales revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), depreciation, and necessary operating expenses.
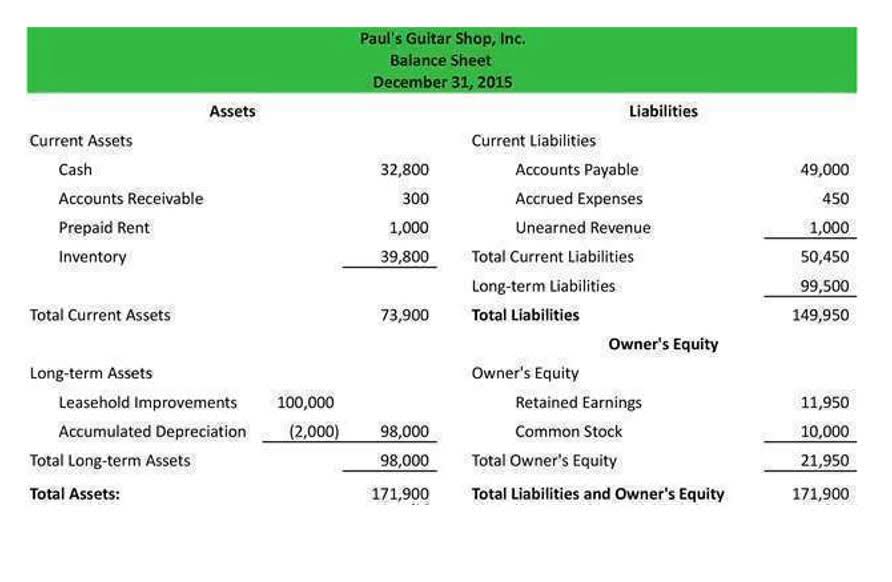
Why does accumulated depreciation have a credit balance on the balance sheet?
- If a company retains earnings but fails to generate a satisfactory return on investment, shareholders may view this as a misuse of funds.
- When a company pays dividends to its shareholders, it reduces its retained earnings by the amount of dividends paid.
- These earnings are reinvested into the business or used to pay down debt and improve financial stability.
- Accumulated earnings are the profits a company retains after paying dividends to shareholders.
- For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, companies with strong balance sheets and significant retained earnings were better positioned to weather the economic shock.
Dividend distributions signal strong financial strength within the company while retained earnings can be used to further future growth. The desired strategy may depend on the amount of profit generated and the potential for value-maximizing projects. On TechBuddy’s balance sheet, the equity section would reflect the new retained earnings (undistributed profits) of ledger account $70,000. The company might also issue a “Statement of Retained Earnings” to show the changes in retained earnings over the course of the year, including the net income earned and dividends paid.
Debt Reduction
This financial resource enables companies to fund growth, reduce debt, and withstand economic downturns. While surplus reserve and undistributed profit both represent portions of a company’s profits that are not distributed to shareholders as dividends, they have distinct attributes that set them apart. One key attribute of surplus reserve is that it is a voluntary action taken by the company’s management. Companies can achieve this by reinvesting profits back into the business to fund expansion projects, research and development, or acquisitions. In scenarios where a company pays out dividends, the net income may not align with retained earnings.
Accumulated Earnings and Shareholder Equity

Regarding the form of capital increase, the law does not specify or limit specific forms of capital contribution. Therefore, the owners/capital contributors/shareholders can contribute capital through the conversion of undistributed profits are not contrary to the law. Retained earnings are the portion of a company’s cumulative profit that is held or retained and saved for future use. The accumulated earnings of a firm are profits generated, but not distributed to the shareholders as cash dividends or as corporate profit taxes. Instead, they are retained to be reinvested in a new business opportunity, to increase inventory levels, to lower long-term debt or to increase cash reserves.

In 2012, Apple announced a dividend program and a share repurchase program, marking a shift in its approach to capital allocation. Since then, Apple has returned hundreds of billions of dollars to shareholders while continuing to retain a portion of its earnings for strategic investments. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, companies with strong balance sheets and significant retained earnings were better positioned to weather the economic shock. They could use their retained earnings to cover fixed costs, invest in digital transformation, and adapt to changing market conditions. The issue of bonus shares, even if funded out of retained earnings, will in most jurisdictions not be treated as a dividend distribution and not taxed in the hands of the shareholder.

Retained Earnings: Everything You Need to Know for Your Small Business

Due to the nature of double-entry accrual accounting, retained earnings do not represent surplus cash available to a company. Rather, they represent how the company has managed its profits (i.e. whether it has distributed them as dividends or reinvested them in the business). When reinvested, those retained earnings are reflected as increases in assets (which could include cash) or reductions to liabilities on the balance sheet. In summary, surplus reserve is a strategic financial tool that companies use to set aside a portion of their profits for future use. It provides a financial cushion for the company, helps fund growth initiatives, and demonstrates the company’s commitment to long-term financial stability. In the United States, the tax treatment of undistributed profit can influence a company’s decision to retain or distribute earnings.
Surplus Reserve vs. Undistributed Profits
Retained earnings, on the other hand, refer to the portion of a company’s net profit that hasn’t been paid out to its shareholders as dividends. When a company consistently experiences net losses, those losses deplete its retained earnings. Prolonged periods of declining sales, increased expenses, or unsuccessful business ventures can lead to negative retained undistributed profits that have accumulated in the company over time are called earnings. Retained earnings, at their core, are the portion of a company’s net income that remains after all dividends and distributions to shareholders are paid out. In a firm’s balance sheet, the retained earnings are accounted under the shareholders’ equity. One key attribute of undistributed profits is their role in supporting the long-term growth and sustainability of a business.
The amount of undistributed profits or retained earnings is reported on a company’s balance sheet under the equity section. This amount is also often disclosed in the statement of retained earnings, which shows the changes in retained earnings over https://www.bookstime.com/bookkeeping-services/vancouver a specific accounting period. Undistributed profit is an important source of capital for companies, as it provides a pool of funds that can be used to support the company’s operations and growth initiatives.

Leave A Comment